What is marketing?
Marketing is the process by which individuals and groups obtain what the need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others.
Marketing: Sustained delivery of customer satisfaction.
Marketing management philosophies
- Production concept: Favor products that are available and highly affordable.
- Product concept: Favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and innovative features.
- Selling concept: Favor products only if the company promotes/sells these products.
- Marketing concept: Focuses on needs/wants of target markets & delivering satisfaction better than competitors.
- Societal marketing concept: society (human welfare), consumers (want satisfaction), company (profits)
Evolution of marketing
- Product philosophy
- Selling philosophy
-
Marketing philosophy
“Everything starts with the customer” -Lou Gerstner, CEO of IBM
“There is only one valid definition of business purpose: to create a customer” -Peter Drucker
“We don’t want to satisfy our customers, we want to delight them.” -Jeff Bezos
“Any business with delighted customers has a sales force they won’t have to pay; You don’t see them, but they are talking to people all the time” -Warren Buffet, 2016
“Creating shareholder wealth is not the purpose of the business. IT is the reward for creating customer value” -Michael Tracey & Fred Wiersema, FEO magazine
FOUR ACTIONS FRAMEWORK
Used to reconstruct buyer value elements in crafting a new value curve or strategic profile
- Raise
- Create
- Eliminate
- Reduce
More on this: https://www.blueoceanstrategy.com/tools/four-actions-framework/
The marketing framework
- Situation analysis
- Customers
- Competitors
- Collaborators
- Company
- Complementors
- Context
- Marketing strategy
- Segmentation
- Targeting
- Positioning
- Marketing tactics
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotions
Delight the customer. in-market testing: slow, expensive. Marketing myopia
What is our product? What do we supply? What is our market? (demand) Who do we sell our products to ?
ABC TV Example.
Marketing Jobs:
- 10% The job is to make this exchange process possible (startups)
- 90% To increase the efficiency of the marketing exchange
Marketing strategy
Demand analysis
Supply programs
- Product line decision
- Distribution decisions
- Marketing mix
- Price decisions
- Communications decisions
Performance metric model
Cause
-
Marketing mix
-
Independent variables
- Competition
- Tasts
- Legal
- Economy
- Cultural
- Socio/economic
Effects
- Behavioral response
- Awareness
- Interest
- Purchase
- Satisfaction loyalty
- Performance measure
- Sales
- Profit (ROI)
- Market share
- BPI
- Benefit/cost
- Image
{insert image in notes}
Market Share = My Sales / Industry Sales
Relative Market Share = My Sales / Competitor Sales
Read more about Boston Consulting Group
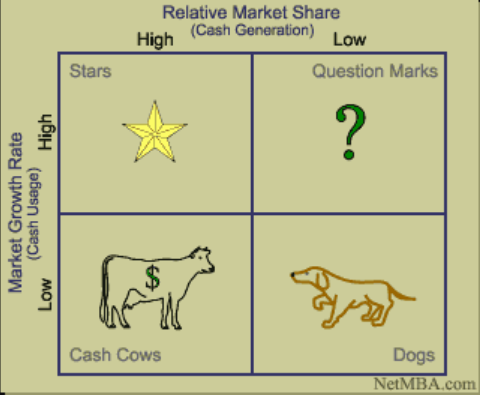 Source: http://www.netmba.com/images/strategy/matrix/bcg/growthshare.gif
Source: http://www.netmba.com/images/strategy/matrix/bcg/growthshare.gif
Structured way to think creatively
| Current Product | New product | |
|---|---|---|
| Current Market | Increase market share, Increase product usage, frequency of use, quantity, new applications | Product improvements, product line extenions, new prod for same market |
| New Market | Expand market for existing prods. Geographic expansion. Target new segments | Vertical integration |
- Market potentiation strategies
- Product development strategies
- Market development strategies
- Diversification strategies
HHI = Market concentration
Guest speaker
Work backwards.
Amazon starts with press release + FAQ and works backwards to creat the product (MVP), then collects feedback.
Amazon workspaces/Smartsheet/Coca-cola freestyle.
{instert story about coca-cola freestyle}
Philosophy of innovation:
- Who they hire
- How the organize (no big teams)
- Use AWS
- Institutional: yes!
- How to think about business opportunities: How BIG is this market? (Not asking what is the ROI first!)
- Willing to fail
Re. business opportunities. Jeff (Amazon CEO) said, “we fully expect to have a $5b failure in the next 5 years”.
Digital transformation
- 40% of the work is structured (ERP, CRM, HCM, ITSM-ticketing, SCM)
- 60% of the work is unstructured or dynamic (brand launches, event planning, employee onboarding, parts ordering, invoice tracking)
How -> Who? (Everyone)
Notes:
- Start with the customer and work backwards
- Focus on solutions, not features
- Design meaningful differentiation
- Be opinionated and adaptable
- Validate with REAL customers before you build
- Ownership == Execution (single threaded ownership)
Domino’s Pizza
great delivery company.
is our pizza good enough. no.
you can use negative comments to let you down or use them to excite you.
our pizza had to be significantly better than both of our two main competitors
The problem Customers did not like the pizza. Marketing metrics showed that Domino’s Pizza was viewed as a great delivery company. The goal was to be a great pizza company.
The solution Use customer insights to create entirely new pizza and brand image. It began a two year program to reinvent its brand.
Experimental design. Marketing metrics is the set of measures that helps marketers quantiry, compare, and interpret their performance.
Domino’s Pizza produced a series of ads based on telling consumers the truth about the old Pizza formulation and what changed. The company returned to the focus group that harshly criticized the old product and surprised them with the new and improved pizza. “Oh yes we did.”
First act of the play: “Tell people the truth.”
Second act: “Bring the new pizza to those who didn’t like it.
The honesty and transparency that the ads pushed, resulted in them being picked up and discussed in a variety of secondary media srouces, resulting in free media. “Second media plan” = Media you don’t pay for.
Buyer/Consumer Behavior
Of these, the cultural factors exert the broadest and deepest influence.
- Cultural factors
- Social Factors
- Reference groups Primary (family friends neighbors, coworkers) Secondary (religious, professional, trade-union) Aspirational groups are a person hopes to join. People are also influenced by groups to which they don’t belong. Dissociative groups are those whose values or behavior an individual rejects.
- Cliques: Small groups whose members interact frequently. They are sometimes insulated from new ideas.
- Family: Family members constitute the most influential primary reference group.
- Family of orientation. Parents and siblings. From parents a person acquires an orientation toward religion, politics, economics a sense of personal ambition, self-worth and love. Family of procreation: Spouse and children. For expensive products and services such as cars, vacations, housing. **Roles and status: Family, clubs, organizations, these are often an important source of information and help define norms of behavior. A role consists of the activities a person is expected to perform. Each role in turn connotes a status.
- Personal Factors
- Age and stage in the life cycle
- Occupation and Economic Circumstances
- Personality and self-concept: Brand personality
- Lifestyle and values
Brand personality: specific mix of human traits that we can attribute to a particular brand. Consumers ofter choose and use brands with personality that is consistent with their actual self-concept (how we view ourselves).
Lifestyle: Is a persons pattern of living in the world as expressed in activities, interests and opinions.
Perception is the process by which we select, organize, and interpret information inputs to create a meaningful picture of the world.
Psychological processes
Marketing and environmental stimuli enter the consumer’s consciousness, and a number of psychological processes combine with certain consumer characteristics to result in the decision processes and purchase decisions. Four key psychological processeslong motivation, perception, learning, and memorylong fundamentally influence consumer responses
Consumer responses are influenced by five key major psychological processes:
- Motivation, can be Biogenic. It arises from physiological states: hunger, thirst, discomfort.
- Perception
- Learning
- Emotions
- Memory
A need becomes a motive when it is aroused to a sufficient level of intensity to drive us to act.
Sigmund Freud assumed the psychological forces shaping people’s behavior are largely unconscious and that people cannot fully understand their own motivations.
Abraham Maslow south to explain why people are driven by particular needs at particular times. Human needs are arranged in hierarchy from most to least pressing: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs.
Frederick Herzberg developed a two-factor theory that distinguishes dissatisfiers from satisfiers. The absence of dissatisfiers is not enough to motivate a purchase.
Selective attention:
Consumer buying process
The stage? model, which outlines the stages of the? consumer-decision process, is composed of five stages. These are problem? recognition, information? search, evaluation of? alternatives, purchase? decision, and? post-purchase behavior.
- Problem Recognition
- General Need Description and Product Specification
- Supplier Search
- Proposal Solicitation
- Supplier Selection
- Order-Routine Specification
- Performance Review
- Information search
- Evaluation of alternatives
- Purchase decision
- Postpurchase behaviour
Behavioral Decision Theory and Behavioral Economics
BDT has identified many situations in which consumers make seemingly irrational choices.
Decision heuristics Framing: Mental accounting
Total Customer Satisfaction
In general, satisfaction is a personâs feelings of pleasure or disappointment that result from comparing a product or serviceâs perceived performance (or outcome) to expectations.
Marketing is ultimately the art of attracting and keeping profitable customers. The case for maximizing? long-term customer profitability is captured in the concept of? The case for maximizing? long-term customer profitability is captured in the concept of customer lifetime value. It describes the net present value of the stream of future profits expected over the? customer’s lifetime purchases. Customer lifetime value (CLV) describes the net present value of the stream of future profits expected over the customerâs lifetime purchases
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Customer_lifetime_value
There are five key ways a company can use and maximize database? marketing: identifying? prospects, segmenting? customers, deepening customer? loyalty, reactivating customer? purchases, and avoiding customer mistakes.
Zappos
Problem. Primarily focused on word of mouth. Darrin Shamo: Senior search engine manager Frequent change in consumer behavior. Marketing costs are rising. Don’t’ understand marketing costs.
The solution. Right message, right time. Tried to get away from demo targeting and geo targeting Instead they allowed them to define the clusters. Attracting the right people. Ads in search engines? Comparison engine vs search engine. Comparison engine: fee based. Brand vs merchant loyalty. Ability to tgrack users at multiple points and channels. Put together a model.
Business and consumer markets
Consumers are better educated and better informed than? ever, and they have the tools to verify? companies’ claims and seek out superior alternatives.? Customer-perceived value is the difference between the prospective? customer’s evaluation of all the benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives.? Customer-perceived value is not something that can be tracked this way.
The business market consists of all organizations that acquire goods and services used in the production of other products or services that are? sold, rented, or supplied to others. The consumer market consists of all organizations that buy or acquire finished products and services.
Business marketing is highly competitive. One of the most critical and fundamental steps in? business-to-business marketing is to create and communicate relevant differentiation from competitors. One of the ways commoditization can be avoided is to differentiate and convince target markets that your product or service is different.
Business Buying Situations
- Straight rebuy
- Modified buy
- New task
Unilever 168,00 employees 170 countries
Glocal.. global and local combine.
Balancing standardization with customization, while it can be tempting to use the same (global) strategy everywhere, localizing has produced successful results.
BOP = bottom of the pyramid = developing countries poorest section of the population. often less than $2,000 us dollars per year.
BOP pays high prices for daily necessities. contributing to the cyclical nature of their poverty.
Unilever is re-targetting to BOP. They hire locals to assist in developing products, services and distribution, and othe infrastructure and improve economic conditions and the lives of the consumers.
Firm can play a substantial role in addressing global poverty.
Unilever pioneered serving the locals by providing to the local sensitivities.
Hindustan Lever (Unilevers Indian subsidiary) leader in
Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning
Define these: A. targeting B. branding C. positioning. Positioning is the act of designing a companies offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the minds of the target market. D. segmentation E. differentiation
The value creation and delivery sequence consists of three phases. In the first phase, choosing the value, marketers segment the market, select the appropriate target, and develop the offerings value positioning.
Perceptual maps are visual representations of consumer perceptions and preferences. By overlaying consumer preferences with brand perceptions, marketers can reveal “holes” or “openings” that suggest unmet consumer needs and marketing opportunities.
Segmentation (Slaying the Mythical Beast)
Employing a process of dividing a heterogeneous market into homogeneous subsets of customers – or segments.
Demographics: We are not alike!
"The Star belly Sneetches had bellies with stars, the plain belly Sneetches had non upon thars..."
Book: The Sneetches by Dr. Seuss
Average JoeLinea: Traditionally we characterized the market by the needs of this mythical creature. Who or What is this? Does this beast exist?
I created a product for the average person, but the average person does not exist. (Average JoeLina.)
By creating
Need a more useful message.
We are not all satisfied by the same things.
Diving a market into groups of potential buyers who have similar:
- needs an wants
- value perceptions
- purchasing behaviors
Segments:
Members are different between segments but similar within.
Campbell Soup & Curtis Publishing Co. Charles curtis parlor (parlen prize, given by the … , equivalent of the nobel prize) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curtis_Publishing_Company http://trashtidbits.blogspot.com/2008/03/campbell-soup-garbage.html
"More than 125 years have passed since advertising pioneer N.W. Ayer conducted the first organized marketing research project in 1879. A second important milestone is the development of marketing research occurred 32 years later, when Charles C. Parlin organized the nation's first commercial research department at Curtis Publishing Co., publisher of The Saturday Evening Post.
Parlin got his start as a marketing researcher by counting soup cans in Philadelphia's garbage. Here is what happened. Parlin, an ad salesman, was trying to convince the Campbell Soup Co. to advertise in The Saturday Evening Post. Campbell Soup resisted, believing that the Post reached primarily working-class readers, who preferred to make their own soup. Campbell Soup marketers were targeting higher income people who could afford to pay for the convenience of soup in a can. To prove Campbell wrong, Parlin began counting soup cans in the garbage collected from different neighborhoods. His research revealed that working-class families bought more canned soup than wealthy households, who had servants to cook for them. Campbell Soup soon became a regular Saturday Evening Post client. It is interesting to note that garbage remains a good source of information for marketing researchers even today. Prior to recent cutbacks in food service, some airlines studied the leftovers from on board meals to determine what to serve passengers."
For 60 years, Campbell’s was a loyal … customer after
(Source: Boone & Kurtz. Contemporary Marketing, 2006.) Saturday evening post. (THE magazine of the US)
Who are our customers?
Do you know who YOUR customers are?
Princess grace kelly (why was this here?)
GICO-> Garbage In, Garbage Out
Pricing strategies
A. Discount pricing B. Perceived-value pricing C. Markup pricing D. Auction-type pricing E. Variable pricing
Tactic: ? Lack-of-demand pricing B. Anticipatory pricing C. ?Over-demand pricing D. Hedge pricing E. Reduction of discounts
CMO: Your tasks include: estimating demand, choosing between cost-based and value-based pricing, selecting an initial price for the product based on available cost data, and adjusting the price based on changes in the market The first factor to consider in pricing is who your demographic is You next move on to estimating demand Now you examine the costs Market Penetration Pricing: Charge a lower price in order to gain market share Market Skimming Pricing: Charge a higher price in order to make more profit quickly.
BCG growth-share matrix approach.
Ieta model … interest, desire, action… in e-trade
learn about : https://www.blueoceanstrategy.com/about-the-authors/ four actions framework: https://www.blueoceanstrategy.com/tools/four-actions-framework/
A leverageable advantage is one that a company can use as a springboard to new? advantages; competitive advantage is a? company’s ability to perform in one or more ways that competitors cannot or will not match
Computer program vs product
“The difference between God and larry ellision” by mike wilson Ed Oates, Founder of Oracle in
Key learnings
Core product needs to be appealing to targeted customer segment. Monopoly is easy: false loyals.
In competitive environment products cannot be customized to all customer segments
- Easy to get greedy and target too many segments with one product
-
word of mouth is missing. product lacks the “oomph”
- Need strategies to grow the market
- pioneering
- Growing the pie: whose job?
Who is responsible for growing the market?
What CMOs claim marketing does
It;s not an expense but an investment. What is the dialog you need to have?
Boards have neglected marketing
- Discussions about cusomters are purely anecdotal
- Need to get in the coversation
Boards spend less thatn 10% of ther time on marketing.
CEO’s and Board’s attention is dominated by Finance.
Poor marketing strategies -> Destroys shareholder value
Impediments to merges and acquisitionA
Synergy: Synergy is the creation of a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts. The term synergy comes from the Attic Greek word s??e???a synergia[1] from synergos, s??e????, meaning “working together”.
Empty chair: the conversation changer… Amazon CEO had an empty chair https://www.inc.com/john-koetsier/why-every-amazon-meeting-has-at-least-one-empty-chair.html
Apostles and Terrorists
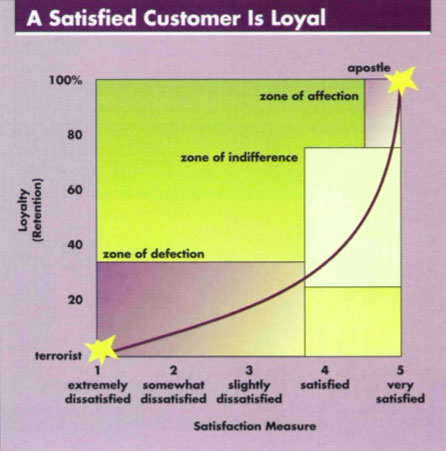
University of michingan database.
https://blog.startquestion.com/understand-customer-loyalty-with-the-apostle-model-618f50dd7423
Starbucks Case…
FACD. Facts Assumptions Calculations Derived
Ref: Heskett et al (1994)
Balacnce short term vs long term
-
Competitive advantage: destroying standard economic theory
-
Createivy: time to think, 15% rule: sabbatical rule 1/7
Marshmallows… story… you can get 1 marshmalleow right now, or two in 15 minutes… way more sucesful… am i willing to give up something () https://www.theatlantic.com/family/archive/2018/06/marshmallow-test/561779/
If my employees are happy, they will take care of my customers.
Employees unhappy -> Customer dissapointed -> complaints -> employee unhappy … {insert picture from notebook}
Expectancy discomformation model
Performance -> discomformation <- expectations
|
Satisfied/disatisfied
Deviation from the expectation
Dimensions for customer service
- Reliability
- Assurance
- Tangibles
- Empathy
- Responsiveness
ACSI
Do employees understand what customers value in service? Customer satisfaction and stock prices ACSI - American Customer Satisfaction Index. 1% change in ACSI associated with 4.6% in market value.
“The only purpose of a business is to create a customer”
Cusetomer markets and consumer loving behaviour
Profitability Loyalty
[loyalty](https://mymarketingcloud.files.wordpress.com/2015/01/customer-relationship-groups.png “”)
Customers -> Cash flows
Customers are assets Not renewing subscription = churn
{insert Profit per customer from notebook}
“Who cares about the numbers, what’s the story?”
80% of your value is generated by 20% of your customers.
[CLV = m ( n / (1 + i - r) )] - AC
Platform shifts and network effects Internet. The mother of all platform shifts How to create network effects?
The endowment effect
{insert story of cup}
Sellers -> $7 Choosers -> $3
(Once you own something you value it more)
Predictably irrational. Anchoring -> social security Day care problem -> Fine Brand strategy. Rationale choice theory.
- Independence of irrelevant alternatives
- Principle of regularity
- Similarity hypothesis
- Assimetry constructed decoy
Pricing behaviour start PPTX
{Insert head nodding story (tuition)>}
Innovation
How innovations spread Consumer resistance / adoption Forecasting innovation diffusion
Product life cycle {insert graph from notebook}
Crossing the chasm Technology adoption life cycle
- Innovators
- Early adopters
- Early majority
- Late majority
- Laggards
Difussion process (show math model)
- 1497: Vasco Da Gama
- Salied around the cape of good Hope
- 160, 100 died
- 1601: Captain Lancaster
- lemon: 3 ships control group
- 1747:
- 1795: British
- Citrous fruit
BASS model applications BASS diffusion model DirecTV hires BASS Innovation difussion -> the flow is assumed
St = P x (Remaining potential) + q x Adopters x Remaining potential
st = sales at time p = coefficient of innovation q = coefficient to immitation
{insert graph from notebook} (MNFR, demand, surplus, marketing effort)
Radical innovation or discontinuous innovation vs Continuous innovation
How do you do sales forecasts on radical innovations? Radical innovation: changin ow users interact.
AIETA: Hierarchy of effects
- Awareness
- Interest
- Evaluation
- Try
- Adoption
Innovation characteristics (for radical innovations?):
- Advancate
- Percieved complexity
- Compatibility
- Observability of advantages
- Risk
- Degree of triability
Amazon’s empty chair. The customer who can’t say anything.
The 9x effect: how many times do i need to visit the cusomter before they….
Pricing
3 types of pricing methods:
- Cost based pricing: Product -> Cost -> Price -> Value -> Customers
- Competition based pricing
- Customer based pricing: Perceived value, value pricing
Price discrimination
- 1st degree
- Prices set for each buyer and each unit
- Extract all consumer surplus -> perfect discrimination
- 3rd degree
- Selection by indicators
- 2nd degree (indirect)
- Cannot observe the characteristics: self-selection
Dynamic product pricing
Market
Psychology of pricing
Prices that en din 9
Prospect theory (nobel price)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prospect_theory
Some implications:
- Bundle losses
- Separate gains
- Bundle small loss with large gain
- Bundle small gain from large loss
Creativity
Creativity: Resource constrained world
The alexandria light house https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lighthouse_of_Alexandria Stratatus….
Childrens Roundabout Water prolbem in remotes areas
Edisons Gate: https://boards.straightdope.com/sdmb/showthread.php?t=127342 https://www.innovationinpractice.com/innovation_in_practice/2014/06/innovation-through-task-unification.html
DMP: What drives our decisions?
- Competition or customers
- Discipline: Easy to get off track, hard to stay focused
Are you driven by what customers want or by what the competition is doing?
The dominance trap.
“Superior experience” to their customers.
Firms: 80% of believed that they dlieverrd (n=326, firms, bain & co) Customers: rated only 8% as delivering this! How customers react/think is often different
Effort to satisfy customers, emmployees and owners
a tale of 3 companies, one served the owners, one the customers and the last (and best performant) a combination.
most is driven by employee satisfaction…
{the virtuous circle slide insert}
“You can count on us to combine a strong quantitavie and analytical culture with a willingness to make bold decisioins. As we do so, we’ll start with the customer and work backwards, in our judgement, that is the best way to create shareholder value”. Jeff Bezos
New management concern: employees & customers.
- be careful how tyou treat your employees
-
understanding your customers: you are not the customer!!!!
- PRoactive vs. Reactive
- Think outside the box
- Framing/Metadecision -> Don’t plunge in (Ex: Pepsi & John Sculley) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Sculley
https://www.amazon.com/Decision-Traps-J-Edward-Russo/dp/0385248350
“The gods must be crazy”
Pepsi, the 2 liter bottle… https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two-liter_bottle .. pepsi.
Dont feel compelled to React on the Dimension on which you have been attacked.
A new word
- Competensity:
-
Brings together competition, intensity and competence.
- Creatrive Destruction
- Average life of Fortune 500 multinational is only 40-50 years (This is why microsoft is re-setting iteself?)
Aristotle: “Whom the gods want to destroy, they first send years of success”
Dominance trap…
A breave new world
-
New reality: Global standards; non-level playing fields; intense rivalry; winners and losers.
- Constant improvement to stay on top.
- Those who don’t serve (customers) well end up losing
-
Not just distance but the direction
- Intelligence:
- Learning from our defeats is obvious.
- enjoy your victories, but learn from – victories and defeats.!! – “too often we fail to appreciate the reasons for our successes”
- Lucky: need to be marginally “smarter” than the competition
Left brain:
- Analtyic
- Logic
- Lang
- Science + math
Right brain:
- Holistic thought
- Intuition
- Creativity
- Art + music
Focus on strategic issues. Focus on market. Competitive ennvironment.
Final words
Reality of the new flux.
"If we wait for all the waves to subside before we enter the ocean for a batn, then we will never be able to enter the ocean at all, brave the waves and enter the ocean"
Ancent tamil proverb
- CEO&F
CEO ===== Customers Employees Owners
CEO&F === Friends and Family
- Have balance
- Blend: CEO And 2Fs
- Great FOE
Have a fascinating journey: don’t be afraid to make mistakes, just make sure you learn from them.
Brand Development Index: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brand_development_index Category Development Index:
Product mix: width, depth, length, and consistency dimensions
What is co-branding? Marketers often combine their products with products from other companies in various ways. In co-branding & also called dual branding or brand bundling & two or more well-known brands are combined into a joint product or marketed together in some fashion.
For co-branding to succeed, the two brands separately must have brand equity (adequate brand awareness and a sufficiently positive brand image).
To organize:
Segmentation Marketing framework !!!! Buy behaviour
Marketing framework: 6cs : customers, complementors, company, competitors, collaborators, context
4ps: product, place/channel/promotion, pricing.
classing example: kim kardashian - pair of flip flops, cristals, $5,000 pair of flip flops. placebo effects on pricing….
Customer acquisition, customer retention, profits
Integrated marketing strategy
- Strategy and tactics be in sync
- choice of one of 4ps affects the others
PLC => Product Lifecycle
https://marketbusinessnews.com/financial-glossary/five-cs/ https://hbr.org/1998/11/business-marketing-understand-what-customers-value